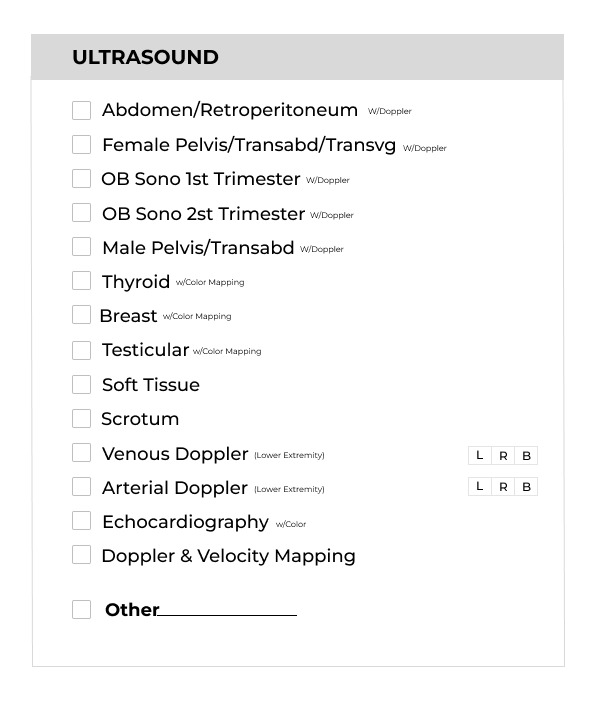
Ultrasound is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that employs high-frequency sound waves to create real-time images of internal structures within the body. During the procedure, a transducer, which emits and receives sound waves, is placed on the skin, allowing the waves to penetrate the body and bounce back as echoes. These echoes are then converted into dynamic images on a monitor, providing detailed views of soft tissues, organs, and blood flow. Widely used across medical specialties, ultrasound is particularly valuable in obstetrics for monitoring pregnancies, assessing fetal development, and detecting abnormalities. In addition to its application in obstetrics, ultrasound is employed in cardiology, gastroenterology, and musculoskeletal imaging. Its versatility extends to guiding minimally invasive procedures, such as biopsies and drainage, due to its real-time imaging capabilities. The advantages of ultrasound include its safety, absence of ionizing radiation, and suitability for repeat examinations. This imaging modality plays a crucial role in diagnostic assessments, aiding healthcare professionals in evaluating a range of conditions